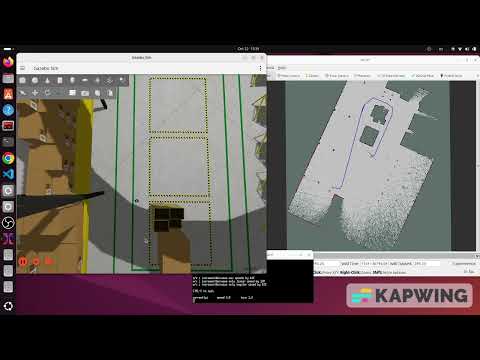
Diff_robot_project_SLAM_Mapping
A quick demonstration of ROS2 SLAM Toolbox in action! Differential drive robot performs real-time mapping using LiDAR and publishes the resulting map to RViz2. See how the robot builds its environment map dynamically and stores it as map.yaml and map.pgm for later navigation.
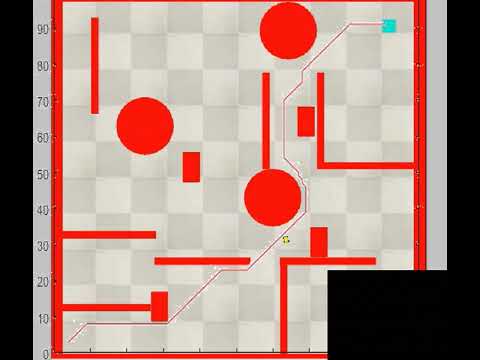
Robot Path Planning: Navigating Obstacles to Reach the Goal
A mobile robot is simulated in CoppeliaSim to navigate with obstacle avoidance using vision sensor. The robot then uses the A* algorithm on the environment map to plan the shortest path and successfully reach the goal.
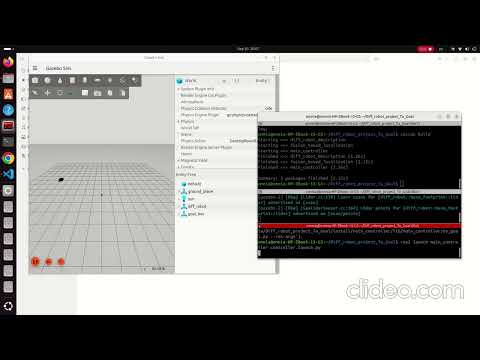
Diff_robot_project_To_Goal
In this project, a differential-drive robot is controlled by two linear PID controllers to reach a specified goal. The controllers publish the robot’s linear and angular velocities based on the error. The movement is simulated in Gazebo, with the goal represented as a black box at the target coordinates (x, y). Path of motion is displayed in Rviz2
Diff_robot_keyboard_move_and_publish_pose
In this project, a differential-drive robot is controlled via the keyboard. The keyboard provides the robot’s center velocity, and the kinematic model computes and publishes the corresponding wheel joint speeds. The movement is simulated in Gazebo, with launch files created for both the controller and the keyboard.
Diff_robot_broadcast_odometry
In this project, a differential-drive robot is controlled via the keyboard. The keyboard supplies the robot’s center velocity, and the kinematic model computes and publishes the corresponding wheel joint speeds. Encoder readings are used to estimate the robot’s new position, orientation, and linear and angular velocities from changes in wheel rotation. These updated values are published as odometry and TF messages for display in RViz2.
Project# Robot Path Planning: Navigating Obstacles to Reach the Goal
In this project, a differential-drive robot is controlled via the keyboard. The keyboard provides the robot’s center velocity, and the kinematic model computes and publishes the wheel joint speeds. Encoder readings estimate the robot’s new pose and velocities from wheel rotations. These odometry updates are published for another node to draw the corresponding trajectory in RViz2.
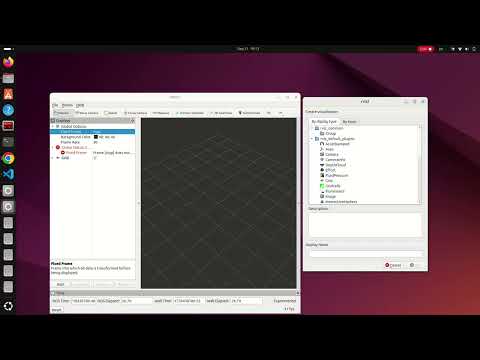
Project# Drift due to_sensor_noise
In this project, we compare ideal controllers with real controllers, accounting for encoder noise and dimensional errors, and display them as two separate TFs in RViz2, along with noise visualization in PlotJuggler.